In the world of international shipping, two key players often come up: NVOCC (Non-Vessel Operating Common Carrier) and Freight Forwarder. While they may seem similar at first glance, their roles, responsibilities, and legal obligations differ significantly. Understanding these differences can help businesses make informed logistics decisions.
1. What is an NVOCC?
An NVOCC (Non-Vessel Operating Common Carrier) is a company that provides ocean freight services without operating its own vessels. Instead, it leases space from ocean carriers and sells it to shippers. In legal terms, an NVOCC acts as a carrier to the shipper and as a shipper to the ocean carrier, serving as an intermediary in the transportation process.
Key Functions of an NVOCC:
· Issues its own House Bill of Lading (HBL) to the shipper.
· Books cargo space from ocean carriers and manages Full Container Load (FCL) and Less than Container Load (LCL) shipments.
· Handles cargo consolidation, deconsolidation, and container management.
· Takes legal responsibility for the cargo during the transportation process.
Since an NVOCC assumes a carrier’s role, it often bears more responsibility than a traditional freight forwarder, especially in terms of cargo liability.
2. What is a Freight Forwarder?
A Freight Forwarder is a logistics service provider that arranges transportation on behalf of shippers. Unlike an NVOCC, a freight forwarder does not act as a carrier but rather as a facilitator, coordinating various aspects of the shipment process.
Key Functions of a Freight Forwarder:
· Organizes multimodal transportation, including ocean, air, rail, and trucking.
· Prepares shipping documents such as customs declarations, bills of lading, and certificates of origin.
· Provides warehousing, cargo insurance, and supply chain management.
· Works with multiple carriers to offer flexible shipping solutions.
Freight forwarders often provide a wider range of services than NVOCCs, including end-to-end logistics and customs clearance. However, unless they have NVOCC status, they typically do not issue their own HBL.
3. Key Differences Between NVOCC and Freight Forwarder
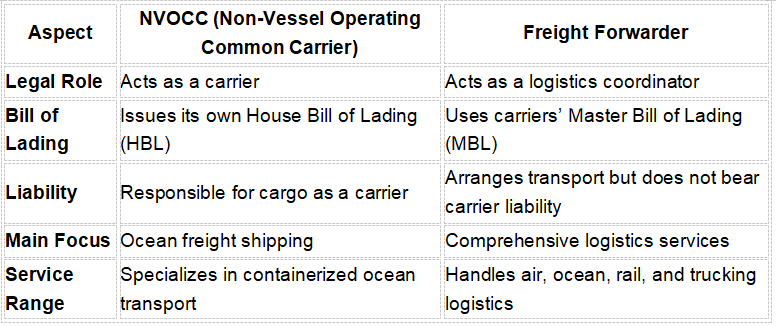
While some companies hold both NVOCC and freight forwarder licenses, they function differently depending on the service agreement.
4. Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between an NVOCC and a freight forwarder depends on your logistics needs:
· For direct ocean freight services with carrier-like responsibilities, an NVOCC is preferable.
· For complete logistics management, including customs, warehousing, and multimodal transport, a freight forwarder is the better choice.
Many businesses work with both NVOCCs and freight forwarders to optimize their supply chain, ensuring efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
5. Conclusion
Both NVOCCs and freight forwarders play crucial roles in global logistics. An NVOCC functions as an ocean carrier, while a freight forwarder provides end-to-end logistics solutions. Choosing the right partner depends on whether your priority is direct carrier services or a broader supply chain solution. By understanding these differences, businesses can make strategic shipping decisions, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.






